Understanding Auto Repair Costs: What to Expect and How to Save – this crucial topic affects every car owner. Unexpected repair bills can be stressful, but with a little knowledge, you can navigate the complexities of auto repair and potentially save money. This guide will explore the various factors influencing repair costs, from labor rates and parts pricing to diagnostic fees and hidden expenses. We’ll also provide practical tips for negotiating fair prices and choosing reliable repair shops, empowering you to make informed decisions and avoid unnecessary costs.
From understanding the nuances of labor rates and the differences between genuine and aftermarket parts, to navigating diagnostic fees and identifying potential hidden costs, we’ll cover it all. We will also delve into the importance of preventative maintenance and offer strategies for finding affordable repair options, ultimately equipping you with the knowledge to confidently handle your vehicle’s maintenance and repair needs.
Understanding Labor Rates
Labor rates are a significant component of auto repair costs, often representing a substantial portion of your final bill. Understanding the factors that influence these rates is crucial for making informed decisions about where to get your vehicle serviced. This section will explore the various elements that contribute to labor rate variations and provide insights into typical costs.
Factors Influencing Labor Rates
Several factors contribute to the variation in labor rates across different repair shops. Geographic location plays a significant role, with higher costs of living and business operation in urban areas often translating to higher labor rates. The type of repair shop also matters; dealerships typically charge more than independent garages due to overhead costs and brand affiliation. The mechanic’s experience and specialization also impact labor rates; highly skilled specialists command higher fees. Finally, the shop’s reputation and customer service levels can indirectly influence pricing, as customers are often willing to pay a premium for quality service.
Geographic Variations in Labor Rates
Labor rates for auto repair vary considerably across different geographic locations. For example, a routine oil change might cost $50-$75 in a rural area, while the same service in a major metropolitan city could range from $75-$120 or even more. This difference reflects the higher operational costs, including rent and employee wages, associated with urban areas. Coastal regions and areas with a high concentration of luxury vehicles may also exhibit higher labor rates due to increased demand and higher-skilled technicians. Consider a hypothetical scenario: a simple brake pad replacement in a small town in the Midwest might cost $200, whereas the same repair in New York City could easily reach $350 or more.
Impact of Specialized Labor Tasks
Specialized labor tasks significantly increase the overall cost of repairs. For instance, diagnosing an electrical issue in a modern vehicle with sophisticated computer systems requires specialized diagnostic equipment and expertise, leading to higher labor charges. Similarly, bodywork repairs, especially those involving advanced techniques like aluminum welding or paintless dent repair, demand highly skilled technicians and specialized tools, driving up the labor costs. Consider the repair of a complex transmission system; the specialized knowledge required, combined with the time needed for disassembly, repair, and reassembly, would significantly increase labor charges compared to a simple oil change.
Hourly Rates for Different Mechanics
The following table compares hourly labor rates for different types of mechanics. These are average estimates and can vary significantly based on location, shop type, and mechanic experience.
| Mechanic Type | Hourly Rate (Low Estimate) | Hourly Rate (Average Estimate) | Hourly Rate (High Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Mechanic | $75 | $100 | $125 |
| Transmission Specialist | $100 | $150 | $200 |
| Electrical Specialist | $125 | $175 | $225 |
| Body Shop Technician | $90 | $120 | $150 |
Parts Costs
Understanding parts costs is crucial for budgeting your auto repair. The price you pay can vary significantly depending on whether you choose genuine manufacturer parts or aftermarket alternatives. This section will explore the key differences between these options, helping you make informed decisions.
Genuine vs. Aftermarket Parts: Price Differences
Genuine manufacturer parts are those produced by the vehicle’s original manufacturer. These parts are typically more expensive than aftermarket parts, which are manufactured by independent companies. The price difference can range from a modest increase to a substantial premium, depending on the part and its complexity. For example, a simple air filter might only cost a few dollars more as a genuine part, while a complex engine component could be significantly pricier. This price difference stems from factors like research and development costs, quality control measures, and branding.
Genuine vs. Aftermarket Parts: Quality and Warranty
Genuine parts are often perceived as offering superior quality and reliability due to rigorous testing and adherence to the manufacturer’s specifications. However, many reputable aftermarket parts manufacturers also produce high-quality components that meet or exceed industry standards. Warranty coverage also differs. Genuine parts usually come with a manufacturer’s warranty, which may vary in length and coverage. Aftermarket parts warranties vary greatly depending on the manufacturer and the specific part. Some aftermarket parts may offer comparable warranties to genuine parts, while others may offer limited or no warranty at all. It’s essential to carefully review the warranty information before purchasing any part.
Factors Influencing Parts Costs
Several factors contribute to the varying costs of specific auto parts. These include the part’s complexity, the materials used in its manufacture, the demand for the part, and the brand reputation. For instance, a technologically advanced electronic control unit will inherently cost more than a simple rubber gasket. Similarly, parts made from high-strength alloys or specialized materials will command higher prices. The availability of the part and its popularity in the aftermarket also influence its cost. Highly sought-after parts or those for rare or discontinued models tend to be more expensive.
Typical Price Differences for Common Car Parts
The table below illustrates typical price differences between genuine and aftermarket parts for common car components. Note that these are estimates and actual prices may vary depending on the vehicle make and model, the retailer, and the specific part.
| Part | Genuine Part (Estimate) | Aftermarket Part (Estimate) | Price Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Filter | $25 | $15 | 40% |
| Brake Pads (Set) | $100 | $60 | 40% |
| Spark Plugs (Set) | $75 | $40 | 47% |
| Headlight Assembly | $250 | $150 | 40% |
Diagnostic Fees
Understanding diagnostic fees is crucial when budgeting for auto repair. These fees cover the time and expertise mechanics spend identifying the root cause of your vehicle’s problems, a necessary step before any repairs can begin. While seemingly an added expense, a proper diagnosis prevents unnecessary repairs and wasted money on parts that don’t address the actual issue.
Diagnostic procedures involve a systematic approach to pinpoint the source of a vehicle malfunction. Mechanics utilize various tools and techniques, from visual inspections and test drives to sophisticated diagnostic equipment that reads the vehicle’s onboard computer system (OBD-II scanner). The complexity of the diagnostic process, and therefore the cost, directly correlates with the difficulty in identifying the problem. A simple check engine light might involve a quick scan, while a complex electrical issue may require extensive testing and troubleshooting.
Diagnostic Procedure Costs and Variations
Diagnostic fees are typically charged hourly or as a flat rate depending on the shop’s policy and the anticipated complexity of the diagnosis. Hourly rates vary regionally and by the shop’s specialization (e.g., independent shops versus dealerships). A simple diagnostic check using an OBD-II scanner might cost between $50 and $100, while more extensive diagnostics, such as those involving specialized equipment or extensive testing, could range from $100 to $300 or even more. For example, diagnosing a persistent electrical fault might involve testing multiple circuits and components, significantly increasing the diagnostic time and, consequently, the cost. Dealerships often have higher hourly labor rates than independent repair shops. The complexity of the issue significantly impacts the final diagnostic fee. A simple, easily identifiable problem like a blown fuse will naturally cost less to diagnose than a complex transmission issue requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
Typical Diagnostic Process Steps
The following steps are involved in a typical diagnostic process:
- Initial consultation and vehicle inspection: The mechanic gathers information about the vehicle’s symptoms and conducts a visual inspection.
- OBD-II scan (if applicable): The mechanic uses an OBD-II scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s computer.
- Further testing and diagnostics: Based on the initial findings, additional tests may be performed, such as checking fluid levels, testing electrical components, or conducting road tests.
- Component testing: Specific components might be tested using specialized equipment to determine their functionality.
- Diagnosis report and explanation: Once the problem is identified, the mechanic provides a detailed report explaining the cause of the malfunction and the recommended repairs.
Common Repair Types and Costs
Understanding the potential costs associated with common car repairs is crucial for responsible vehicle ownership. This section categorizes common repairs by cost and provides examples to help you budget effectively. Remember that these are estimates, and actual costs can vary depending on factors such as vehicle make and model, location, and the specific repair shop.
Common Repair Types Categorized by Cost
Predicting the exact cost of a car repair can be challenging; however, categorizing repairs into low, medium, and high cost ranges offers a useful framework for budgeting. This allows for better financial planning and reduces the likelihood of unexpected expenses significantly impacting your finances.
| Repair Type | Typical Cost Range | Potential Causes | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Cost Repairs | $50 – $500 | Minor issues, regular maintenance | Oil change, tire rotation, wiper blade replacement, headlight bulb replacement. |
| Medium-Cost Repairs | $500 – $2000 | More significant mechanical or electrical problems | Brake pad replacement, battery replacement, exhaust system repair, minor suspension work. |
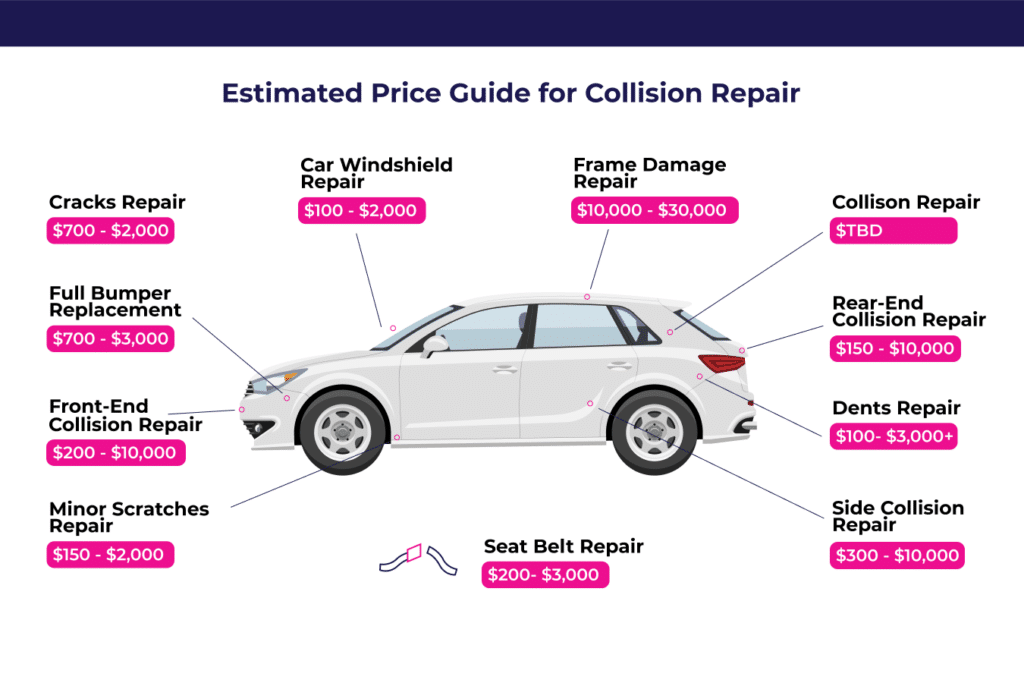
| High-Cost Repairs | $2000+ | Major engine, transmission, or body damage | Engine rebuild or replacement, transmission repair or replacement, major collision repair. |
Unexpected Repairs and Their Potential Costs
Unforeseen car repairs can significantly strain a budget. Understanding potential scenarios and their associated costs helps in proactive financial planning and mitigates the impact of sudden expenses.
For instance, a sudden failure of the alternator (a crucial component for charging the battery) can leave you stranded and require a costly replacement, potentially ranging from $300 to $800 depending on the vehicle and labor costs. Similarly, a catastrophic failure of a water pump can lead to engine overheating and significant engine damage, potentially costing thousands of dollars in repairs.
Another example is a sudden tire blowout. While replacing a tire is a relatively inexpensive repair, the cost can escalate if the blowout damages the wheel rim or other suspension components. Furthermore, a seemingly minor issue like a failing fuel pump can lead to significant repair costs if not addressed promptly, potentially leading to engine damage.
Typical Repair Costs for Specific Systems
Understanding the typical costs associated with repairs to major vehicle systems such as the engine, brakes, and electrical components is vital for effective budgeting.
| System | Typical Cost Range | Potential Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Issues | $500 – $10,000+ | Wear and tear, lack of maintenance, overheating, mechanical failure. This range accounts for minor repairs like a sensor replacement to major repairs such as engine rebuild or replacement. |
| Brake Repairs | $100 – $1000+ | Worn brake pads and rotors, fluid leaks, malfunctioning calipers or master cylinder. |
| Electrical Problems | $100 – $2000+ | Faulty wiring, alternator failure, battery problems, sensor malfunctions. The cost range varies widely depending on the complexity of the issue. |
Hidden Costs and Unexpected Expenses
Auto repair costs can sometimes extend beyond the initial estimate. Several hidden expenses and unforeseen issues can significantly inflate the final bill. Understanding these potential additions allows you to better budget and avoid unpleasant surprises. This section will outline common hidden costs and unexpected expenses you may encounter.
Unexpected issues discovered during a repair often lead to increased costs. The initial assessment might not uncover all problems, and further investigation may reveal additional damage requiring further repair. This is particularly true with older vehicles where multiple components may be interconnected and a single problem can trigger a cascade of related issues.
Unforeseen Repair Discoveries
During a seemingly straightforward repair, mechanics might discover additional problems requiring immediate attention to prevent further damage or safety hazards. For example, a simple brake pad replacement might reveal severely corroded brake lines, necessitating a more extensive and costly repair. Similarly, an engine oil leak diagnosis might uncover a cracked engine block, requiring a costly engine rebuild or replacement. These situations are not uncommon and underscore the importance of thorough diagnostics.
Examples of Unforeseen Expenses
Consider a scenario where a customer brings their car in for a scheduled oil change. During the service, the mechanic notices a significant coolant leak. A further inspection reveals a damaged radiator hose. While the initial estimate only covered the oil change, the additional repair of the hose and coolant refill adds to the overall cost. Another example might involve a car brought in for a simple tire rotation. Upon inspection, the mechanic discovers significant rust and damage to the undercarriage, requiring additional repair work to prevent further deterioration and potential safety issues.
Potential Hidden Costs
It’s crucial to be aware of potential hidden costs that might not be immediately apparent. These can significantly impact the final bill.
- Disposal Fees: Many shops charge extra for disposing of old parts, fluids, and other waste materials, particularly hazardous materials like used motor oil and brake fluid. These fees are often environmentally mandated.
- Environmental Charges: Related to disposal fees, environmental charges cover the proper handling and disposal of hazardous waste generated during the repair process. These charges vary by location and the type of waste involved.
- Shop Supplies: While some shops include the cost of minor shop supplies (like cleaning materials) in the labor cost, others may charge separately for extensive use of these materials.
- Diagnostic Fees: While often included in the initial assessment, some shops charge separately for in-depth diagnostics, especially if the issue is complex or requires specialized equipment.
- Taxes: Sales tax will apply to parts and labor costs in most jurisdictions.
Warranty Coverage and Repair Costs
Vehicle warranties play a significant role in determining your out-of-pocket expenses for repairs. Understanding the different types of warranties and their limitations is crucial for budgeting and managing vehicle maintenance costs effectively. This section will clarify how warranties can impact your repair bills and what to expect in various scenarios.
Types of Warranties and Their Coverage
New vehicles typically come with a combination of warranties, offering protection against defects in materials and workmanship. These often include a bumper-to-bumper warranty, covering most components, and a powertrain warranty, focusing on the engine, transmission, and drivetrain. The duration and mileage limitations vary significantly by manufacturer and vehicle model. Used vehicles may have remaining factory warranties or come with extended warranties purchased by the previous owner or dealer. These extended warranties, also known as service contracts, often provide coverage beyond the original manufacturer’s warranty period but usually come with specific terms and conditions. It’s essential to carefully review the warranty document for specific details regarding covered components, exclusions, and the process for filing a claim.
Situations Where a Warranty Might Not Cover Repairs
Several factors can exclude repairs from warranty coverage. Normal wear and tear is a common exclusion. This includes items like brake pads, tires, and wiper blades that naturally degrade over time due to usage. Damage resulting from accidents, misuse, or neglect is also typically not covered. For example, damage caused by driving through deep water and subsequently causing engine failure would likely be excluded. Furthermore, repairs resulting from lack of proper maintenance, such as neglecting scheduled oil changes, might void or limit warranty coverage. Finally, modifications or aftermarket parts installed without manufacturer approval can also impact warranty validity. Always consult your warranty document for a comprehensive list of exclusions.
Examples of Warranty Coverage Affecting Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Consider two scenarios: In the first, a new vehicle’s engine fails due to a manufacturing defect within the powertrain warranty period. The repair, potentially costing thousands of dollars, would be covered under warranty, resulting in zero out-of-pocket expenses for the owner. In the second scenario, the same vehicle’s transmission fails after the warranty expires due to normal wear and tear. The owner would be fully responsible for the significant repair cost. Similarly, if a used vehicle’s air conditioning system malfunctions due to a pre-existing condition not covered by the existing warranty, the buyer would be responsible for the repair costs. These examples highlight how warranties can drastically alter the financial burden of vehicle repairs.
Negotiating Repair Costs
Negotiating auto repair costs can feel daunting, but with a strategic approach, you can often secure a fairer price. Understanding the factors that influence repair costs, as discussed in previous sections, is the first step towards effective negotiation. This section will equip you with the skills and knowledge to confidently discuss your budget and expectations with your mechanic.
Effective Communication and Budget Setting
Clearly communicating your budget and expectations is crucial for a successful negotiation. Avoid vague statements like “I want it cheap.” Instead, state your budget explicitly, for example, “My budget for this repair is $500, and I’d like to understand how we can work within that limit.” This allows the mechanic to explore options and potentially offer alternative solutions that fit your financial constraints. It also demonstrates your seriousness and willingness to engage in a productive discussion.
Negotiation Techniques
Several techniques can enhance your negotiation skills. One effective strategy is to politely inquire about potential discounts or specials. Many repair shops offer discounts for seniors, military personnel, or those who pay in cash. Another approach involves exploring alternative parts. If the mechanic suggests using a high-priced OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) part, ask about the possibility of using a high-quality aftermarket part, which can often offer significant cost savings without compromising performance or reliability. Remember to maintain a respectful and professional demeanor throughout the negotiation process. A collaborative approach often yields better results than an adversarial one.
The Value of Multiple Quotes
Obtaining multiple quotes from different reputable repair shops is arguably the most effective way to negotiate a fair price. By comparing quotes, you can identify the average cost for the specific repair and pinpoint any unusually high or low estimates. This information provides a strong foundation for negotiating. For example, if three shops quote $400, $450, and $600, you have a solid basis for discussing the $600 quote with the relevant shop, highlighting the lower estimates you’ve received. This demonstrates that you’ve done your research and are aware of market prices. Remember to ensure that all quotes are for the same services and parts to make a fair comparison.
Preventive Maintenance and Cost Savings
Preventive maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of your vehicle and significantly reducing long-term repair costs. By addressing potential problems before they escalate into major breakdowns, you can save yourself considerable expense and inconvenience. Regular maintenance acts as an insurance policy against unexpected and costly repairs.
Regular maintenance tasks, performed according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedule, can prevent costly breakdowns and ensure your vehicle remains in optimal condition. These tasks, while requiring an upfront investment, ultimately save money by preventing more expensive repairs down the line. Neglecting these tasks can lead to premature wear and tear, resulting in far greater expenses in the long run.
Common Preventative Maintenance Tasks and Costs
Preventative maintenance encompasses a range of services designed to identify and address potential issues before they become major problems. These services vary in cost depending on your vehicle’s make, model, and the specific service provider. However, a proactive approach to maintenance generally results in significant long-term savings.
Preventative Maintenance Schedules and Costs
The following table outlines a recommended preventative maintenance schedule and associated costs. These are estimates and can vary depending on location, vehicle type, and service provider. It is always advisable to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for manufacturer-specific recommendations.
| Maintenance Task | Recommended Frequency | Estimated Cost Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 3,000-5,000 miles or 3-6 months | $50 – $150 | Cost varies based on oil type and quantity. |
| Tire Rotation and Balancing | Every 5,000-7,500 miles | $20 – $50 | Improves tire wear and handling. |
| Fluid Checks (Coolant, Brake Fluid, Power Steering Fluid, Transmission Fluid) | Every 3,000-5,000 miles or during oil changes | Included in oil change or $20 – $40 separately | Ensures proper fluid levels and prevents damage to components. |
| Air Filter Replacement | Every 12,000-15,000 miles or as needed | $20 – $50 | Improves engine performance and fuel efficiency. |
| Brake Inspection | Every 6 months or 6,000 miles | $30 – $70 | Identifies potential brake issues early. |
| Spark Plug Replacement | Every 30,000-100,000 miles (depending on vehicle) | $100 – $300 | Improves engine performance and fuel efficiency. |
| Serpentine Belt Inspection and Replacement | Every 60,000-100,000 miles (depending on vehicle) | $50 – $150 | Prevents costly engine damage if it breaks. |
Finding Affordable Repair Options
Finding affordable auto repair services requires careful consideration of various factors and options. The cost of repairs can vary significantly depending on the type of shop you choose, the complexity of the repair, and even the location of the shop. Understanding these variables is key to making informed decisions and saving money.
Independent Shops versus Dealership Service Centers
Independent repair shops and dealership service centers offer distinct advantages and disadvantages concerning cost and service. Dealerships often charge higher labor rates due to their overhead and trained technicians. However, they may have access to specialized tools and genuine parts, potentially leading to a more efficient repair. Independent shops, on the other hand, typically offer lower labor rates and may be more flexible in their pricing. However, the quality of service and parts can vary significantly between independent shops, necessitating careful research and selection. Choosing between these two options depends heavily on your vehicle’s make and model, the type of repair needed, and your budget. For routine maintenance, an independent shop might be a cost-effective choice. For complex repairs requiring specialized knowledge of your vehicle’s make and model, a dealership might offer a more reliable solution, even at a higher cost.
Utilizing Online Resources to Locate Reliable and Affordable Mechanics
The internet provides valuable resources for finding reputable and affordable auto repair shops. Websites like Yelp, Google Reviews, and RepairPal allow consumers to access reviews and ratings from other customers, providing insights into the quality of service, pricing, and overall customer experience. These platforms often include information about shop specializations, services offered, and customer feedback on specific repairs. Additionally, utilizing online search engines with specific keywords such as “affordable auto repair near me” can yield a list of local shops, along with their contact information and online reviews. By carefully reviewing these online resources, consumers can significantly narrow their search and identify shops that best meet their needs and budget.
Researching and Choosing a Reputable Auto Repair Shop
Effective research is crucial in selecting a trustworthy and affordable auto repair shop. Beyond online reviews, consider checking the shop’s certifications and licenses. Look for certifications from organizations like the Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), which demonstrates a commitment to professional standards and ongoing training. Verify that the shop is properly licensed to operate in your area. It’s also advisable to contact the Better Business Bureau to check for any complaints or negative feedback filed against the shop. Before committing to a repair, obtain multiple estimates from different shops to compare pricing and services. Remember to clearly outline the repair needed, including all necessary parts and labor, to ensure consistent comparisons. This diligent research process can significantly reduce the risk of unexpected costs and ensure you receive high-quality service at a reasonable price.
Outcome Summary
Ultimately, understanding auto repair costs is about more than just saving money; it’s about gaining control over your vehicle’s maintenance and repair process. By understanding the factors that influence repair costs, utilizing effective negotiation strategies, and prioritizing preventative maintenance, you can significantly reduce the stress and financial burden associated with car repairs. Remember, informed decisions lead to better outcomes, and this guide provides the knowledge you need to confidently navigate the world of auto repair.